Glossary
Some families may know these words and some families may have never heard them before. Always ask your child’s doctor, nurse, or other health care provider if you don’t understand something they say to you. As providers, we want to make sure all information is presented to you in a way you can understand, so you can make the best decisions for your family.
Acute Respiratory Failure: A condition when not enough oxygen passes from the lungs into the blood or when your lungs cannot effectively get rid of carbon dioxide (a waste product that we exhale in every breath). The body needs enough oxygen in the blood and not too much carbon dioxide to work right. Multiple things can make the lungs sick enough to cause acute respiratory failure, such as severe pneumonia or a severe asthma attack.
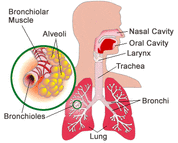
Bronchiolitis: An irritation to the smaller airways that branch from the trachea (windpipe) and bronchi. The bronchi are two tubes that branch off from the windpipe into smaller parts. The trachea and bronchi carry air to the lungs.
Clinical Trial: A research study of humans, where people are assigned to a different groups and receive different medical treatments to evaluate the effects of these medical treatments.
Comfort Medications/Sedatives: A drug prescribed by a doctor to help patients stay calm and/or go to sleep.
Extubation: The removal of the tube in the windpipe. This is done when the extra oxygen or breathing machine is no longer needed.
Intubation: When a tube is placed through the mouth and down into the windpipe. The tube opens up the airway so that more oxygen can be delivered and carbon dioxide can be removed. The tube is used with a breathing machine.
Latrogenic Withdrawal Syndrome: A complication that happens to a person after getting medical treatment including sedative medications. The body can get used to these medicines (which we call developing a tolerance to them) while on the breathing machine. The tolerance may results in physical dependence. That means the body needs the medicine to prevent signs of withdrawal. Signs of withdrawal can include sweating, racing heartbeat and diarrhea. It can also cause nausea, vomiting, rapid breathing, and uncontrolled shaking or tremors. RESTORE is designed to help ease symptoms of iatrogenic withdrawal syndrome for pediatric patients on breathing machines.
Mechanical Ventilation: Mechanical ventilation uses a machine called a ventilator (breathing machine). This machine supplies oxygen to the lungs and helps your child breathe. Healthcare providers can change the size of each breath; the amount of oxygen, and how often a breath is taken that best fit for your child's needs. Breathing machines are one of the treatments of respiratory failure.
National Institute for Health (NIH): Part of the US Department of Health and Human Services that funds and oversees medical research in the United States.
Neurocognitive: Describes the relation between functions of certain areas of the brain.
Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU): An area of a hospital specializing in the care of very sick infants and children.
Pneumonia: An infection in both or one of the lungs. Causes could be from bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Those who are less than two years old or have health problems are more at risk. Signs can include high fever, shaking chills and a cough that does not go away or get better. Other signs can also include chest pain, shortness of breath, and sometimes even abdominal pain.
Post-Traumatic Stress: Is a psychological condition that can occur when a person experiences or witnesses a traumatic event where they were physically harmed, or the threat of physical harm or death was present.
Principal Investigator: Is the lead scientist of a biomedical research study, they direct the study team.
Sedation: Calming medicines. Over 90% of infants and children supported on breathing machines receive some form of sedative therapy. This is often more than one medicine. These medicines include opioids and benzodiazepines.
Bronchiolitis: An irritation to the smaller airways that branch from the trachea (windpipe) and bronchi. The bronchi are two tubes that branch off from the windpipe into smaller parts. The trachea and bronchi carry air to the lungs.
Clinical Trial: A research study of humans, where people are assigned to a different groups and receive different medical treatments to evaluate the effects of these medical treatments.
Comfort Medications/Sedatives: A drug prescribed by a doctor to help patients stay calm and/or go to sleep.
Extubation: The removal of the tube in the windpipe. This is done when the extra oxygen or breathing machine is no longer needed.
Intubation: When a tube is placed through the mouth and down into the windpipe. The tube opens up the airway so that more oxygen can be delivered and carbon dioxide can be removed. The tube is used with a breathing machine.
Latrogenic Withdrawal Syndrome: A complication that happens to a person after getting medical treatment including sedative medications. The body can get used to these medicines (which we call developing a tolerance to them) while on the breathing machine. The tolerance may results in physical dependence. That means the body needs the medicine to prevent signs of withdrawal. Signs of withdrawal can include sweating, racing heartbeat and diarrhea. It can also cause nausea, vomiting, rapid breathing, and uncontrolled shaking or tremors. RESTORE is designed to help ease symptoms of iatrogenic withdrawal syndrome for pediatric patients on breathing machines.
Mechanical Ventilation: Mechanical ventilation uses a machine called a ventilator (breathing machine). This machine supplies oxygen to the lungs and helps your child breathe. Healthcare providers can change the size of each breath; the amount of oxygen, and how often a breath is taken that best fit for your child's needs. Breathing machines are one of the treatments of respiratory failure.
National Institute for Health (NIH): Part of the US Department of Health and Human Services that funds and oversees medical research in the United States.
Neurocognitive: Describes the relation between functions of certain areas of the brain.
Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU): An area of a hospital specializing in the care of very sick infants and children.
Pneumonia: An infection in both or one of the lungs. Causes could be from bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Those who are less than two years old or have health problems are more at risk. Signs can include high fever, shaking chills and a cough that does not go away or get better. Other signs can also include chest pain, shortness of breath, and sometimes even abdominal pain.
Post-Traumatic Stress: Is a psychological condition that can occur when a person experiences or witnesses a traumatic event where they were physically harmed, or the threat of physical harm or death was present.
Principal Investigator: Is the lead scientist of a biomedical research study, they direct the study team.
Sedation: Calming medicines. Over 90% of infants and children supported on breathing machines receive some form of sedative therapy. This is often more than one medicine. These medicines include opioids and benzodiazepines.


